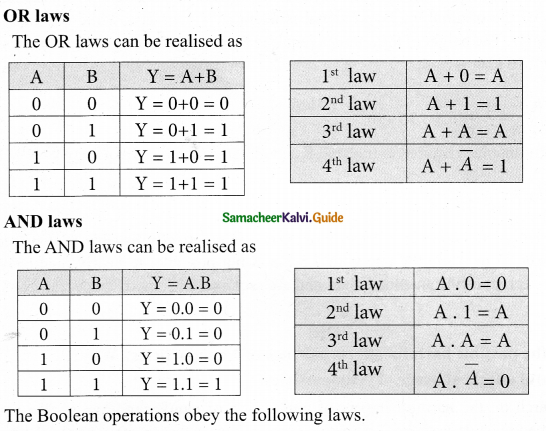
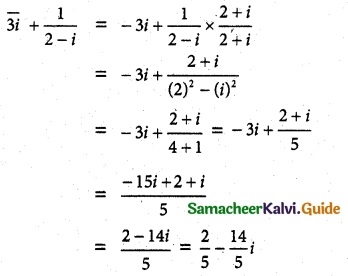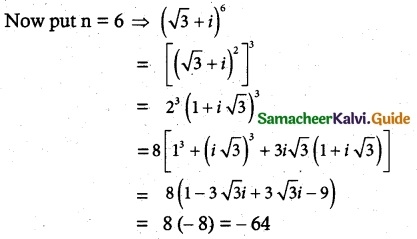Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Complex Numbers Ex 2.5 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Complex Numbers Ex 2.5
Question 1.
Find the modulus of the following complex numbers.
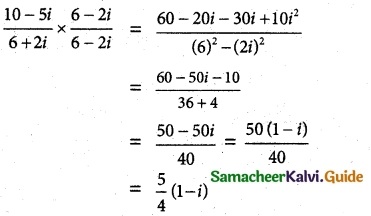
(i) \(\frac{2i}{3+4i}\)
Solution:

(ii) \(\frac{2-i}{1+i}+\frac{1-2 i}{1-i}\)
Solution:
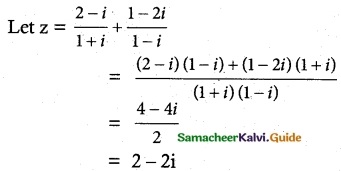
Modulus of z = |z| = \(\sqrt{4+4}\)
= √8
= 2√2
(iii) |(1 – i)10| = (|1 – i|)10
= \((\sqrt{1+1})^{10}=(\sqrt{2})^{10}=2^{5}=32\)
(iv) |2i(3 – 4i) (4 – 3i)|
= |2i| |3 – 4i| |4 – 3i|
= \(2 \sqrt{9+16} \sqrt{16+9}\)
= 2 × 5 × 5
= 50
![]()
Question 2.
For any two complex numbers z1 and z2, such that |z1| = |z2| = 1 and z1 z2 ≠ -1, then show that \(\frac{z_{1}+z_{2}}{1+z_{1} z_{2}}\) is real number.
Solution:
Given |z1| = |z2| = 1 and z1 z2 ≠ 1
|z1|² = 1 |z2|² = 1
z1 \(\bar{z}_{1}\) = 1 similarly z2 \(\bar{z}_{2}\) = 1

Since z = \(\bar{z}\), it is a real number.
![]()
Question 3.
Which one of the points 10 – 8i, 11 + 6i is closest to 1 + i.
Solution:
A (1 + i), B (10 – 8i), C (11 + 6i)
|AB| = |(10 – 8i) – (1 + i)|
= |10 – 8i – 1 – i|
= |9 – 9i|
= \(\sqrt{81+81}\)
= \(\sqrt{162}\)
= 9(1.414)
= 12.726
CA = |(11 + 6i) – (1 + i)|
= |11 + 6i – 1 – i|
= |10 + 5i|
= \(\sqrt{100+25}\)
= \(\sqrt{125}\)
C (11 + 6i) is closest to the point A (1 + i)
![]()
Question 4.
If |z| = 3, show that 7 ≤ |z + 6 – 8i| ≤ 13.
Solution:
given |z| = 3
|z + 6 – 8i| ≤ |z| + |6 – 8i|
= 3 + \(\sqrt{6^2+8^2}\)
= 3 + \(\sqrt{100}\)
= 3 + 10 = 13
∴ |z + 6 – 8i| ≤ 13 ……….. (1)
|z + 6 – 8i| ≥ ||z| – |-6 + 8i||
= |3 – 10|
= |-7| = 7
∴ |z + 6 – 8i| ≥ 7 ………… (2)
from 1 and 2
we get 7 ≤ |z + 6 – 8i| ≤ 13
hence proved.
Question 5.
If |z| = 1, show that 2 ≤ |z² – 3| ≤ 4.
Solution:
|z| = 1 ⇒ |z|2 = 1
||z1| – |z2|| ≤ |z1 + z2| ≤ |z1| + |z2|
||z|2 – |-3|| ≤ |z2 – 3| ≤ |z|2 + |-3|
|1 – 3| ≤ |z2 – 3| ≤ 1 + 3
2 ≤ |z2 – 3| ≤ 4
Question 6.
If |z| = 2 show that the 8 ≤ |z + 6 + 8i| ≤ 12
Solution:
Given |z| = 2
|z + 6 + 8i| = |z| + |6 + 8i|
= 2 + \(\sqrt{6^2+8^2}\)
= 2 + \(\sqrt{100}\)
= 2 + 10
= 12
∴ |z + 6 + 8i| ≤ 12 ……….. (1)
|z + 6 + 8i| ≥ ||z| – |-6 – 8i||
= |2 – 10|
= |-8|
= 8
|z + 6 + 8i| ≥ 8 ………… (2)
From 1 and 2 we get
8 ≤ |z + 6 + 8i| ≤ 12
Hence proved
![]()
Question 7.
If z1 z2 and z3 are three complex numbers such that |z1| = 1, |z1| = 2, |z3| = 3 and |z1 + z2 + z3| = 1 show that |9z1 z2 + 4z1 z3 + z2 z3| = 6.
Solution:
|z1| = 1, |z1| = 2, |z3| = 3
|z1 + z2 + z3| = 1
Now |9z1 z2 + 4z1 z3 + z2 z3|
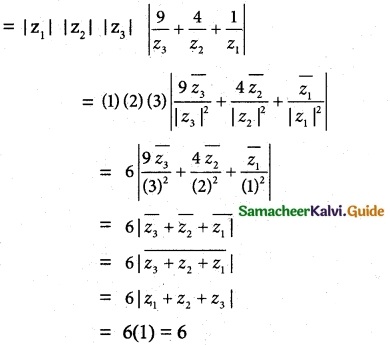
Hence proved.
![]()
Question 8.
If the area of the triangle formed by the vertices z, iz, and z + iz is 50 square units, find the value of |z|.
Solution:
The given vertices are z, iz, z + iz ⇒ z, iz are ⊥r to each other.
Area of triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) bh = 50
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) |z| |iz| = 50
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) |z| |z| = 50
⇒ |z|2 = 100
⇒ |z| = 10
Aliter:
Given the area of triangle = 50 sq. unit
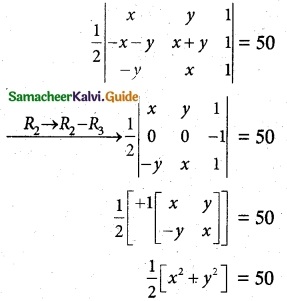
x² + y² = 100
|z|² = 100
|z| = 10
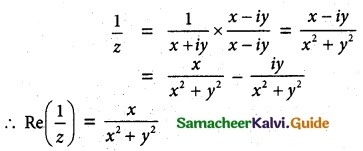
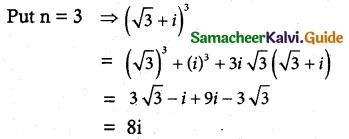
Question 9.
Show that the equation z³ + 2 \(\bar {z}\) = 0 has five solutions.
Solution:
Given z³ + 2 \(\bar {z}\) = 0
z³ = -2 \(\bar {z}\)
|z³| = |-2| |\(\bar {z}\)|
|z|³ = 2|z| [∵ |z| = |\(\bar {z}\)|
|z|³ – 2 |z| = 0
|z| [|z|² – 2] = 0
|z| = 0 |z|² = 2
z\(\bar {z}\) = 2
z = \(\frac{2}{\bar {z}}\) = ± √2 [∵ \(\bar {z}\) = \(\frac{-z^3}{2}\) ]
z = \(\frac{2}{(\frac{z^3}{-2})}\)
z4 = 4
It has 4 non zero solutions.
∴ Including z = 0 we have 5 solutions.
![]()
Question 10.
Find the square roots of
(i) 4 + 3i
Solution:
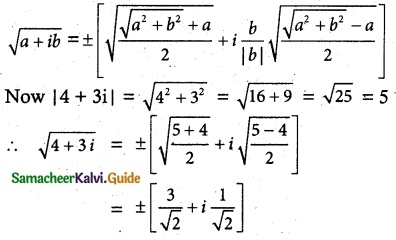
|4 + 3i| = \(\sqrt {4^2+3^2}\) = \(\sqrt {16+9}\)
\(\sqrt {25}\) = 5
Let \(\sqrt {4+3i}\) = a + ib
squaring on both sides
4 + 3i = (a + ib)²
4 + 3i = (a² – b²) + 2 jab
Equating real and imaginary parts
a² – b² = 4, 2ab = 3
(a² + b²)² = (a² – b²)² + 4a² b²
= (4)² + (3)²
= 16 + 9 = 25
∴ a² + b² = 5
Solving a² – b² = 4 and a² + b² = 5.
we get a² = \(\frac {9}{2}\) , b² = \(\frac {1}{2}\)
a = ±\(\frac {3}{√2}\) and b = ±\(\frac {1}{√2}\)
∴ \(\sqrt {4 + 3i}\) = a + ib
= ±(\(\frac {3}{√2}\) + ±\(\frac {i}{√2}\))
Aliter:
Square root of 4 + 3i
formula method
(ii) -6 + 8i
Solution:
Let \(\sqrt {-6 + 8i}\) = a + ib
Squaring on both sides
-6 + 8i = (a + ib)²
-6 + 8i = a² – b² + 2iab
Equating real and imaginary parts
a² – b² = -6 and 2ab = 8
Now (a² + b²)² = (a² – b²)² + 4a²b²
= (-6)² + (8)²
= 36 + 64 = 100
∴ a + b² = 10
Solving a² – b² = -6 and a² + b² = 10
we get 2a² = 4, b² = 8
a² = 2, b² = ±2√2
a = ±√2
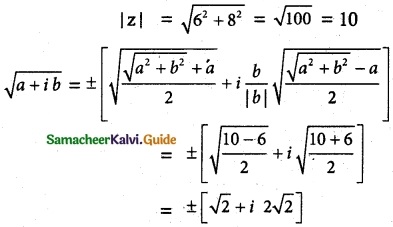
∴ \(\sqrt {-6 + 8i}\) = ±√2 ± i 2√2
= ±(√2 + i 2√2)
Aliter:
square root of -6 + 8i
let a + ib = -6 + 8i
a = -6, b = 8
![]()
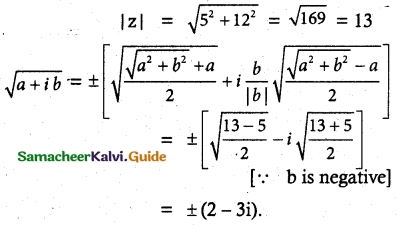
(iii) -5 – 12i
Solution:
Let \(\sqrt{-5-12 i}\) = a + ib
Squaring on both sides
-5 – 12i = (a+ib)²
-5 – 12i = a² – b² + 2iab
Equating real and imaginary parts
a² – b² = -5, 2ab = -12
(a² + b²)² = (a² – b²)² + 4a²b²
= (-5)² + (-12)² = 169
∴ a² + b² = 13
Solving a²- b² = -5 and a² + b² = 13
we get a² = 4, b² = 9
a = ±2, b = ±3
Since 2ab = -12 < 0, a, b are of opposite signs.
∴ When a = ±2, b = ±3
Now \(\sqrt{-5-12 i}\) = ± (2 – 3i)
Aliter
Square root of -5 – 12i
Let a + ib = -5 – 12i
a = -5, b = -12