Students can download 6th Science Term 3 Chapter 5 Plants in Daily Life Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 5 Plants in Daily Life
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Plants in Daily Life Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
One of the following birds is an example of plant-pollinator
a. Duck
b. Parrot
c. Hummingbird
d. Dove
Answer:
c. Hummingbird
Question 2.
Natural Mosquito repellant is
(a) Nutmeg
(b) Bamboo
(c) Ginger
(d) Neem
Answer:
(d) Neem
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a root?
a. Potato
b. Carrot
c. Radish
d. Turnip
Answer:
a. Potato
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following medicinal plants has anti-cancer properties?
(a) Amla
(b) Tulasi
(c) Turmeric
(d) Aloe
Answer:
(c) Turmeric
Question 5.
Which is the national tree of India?
a. Neem tree
b. Jack tree
c. Banyan tree
d. Mango tree
Answer:
c. Banyan tree
II. Fill in the Blanks
- In every year October ……….is celebrated as world food day.
- ………… is an example of textile fibre.
- I am the state tree of Tamilnadu. Who am I ………… ?
- The juice of the leaves of ……… plant relieves cough and bronchitis.
- The edible seeds of leguminous plants are called …………
Answer:
- 16
- Cotton
- Palm tree
- Tulsi
- pulses
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement.
- Plants grown for decorative purposes are called as softwood.
- Silkworm eats mulberry leaves.
- Cauliflower is used for ornamental purpose.
- Cotton cloth is not suitable for summer season.
- Sugarcane is used as biofuel.
Answer:
- False – Plants grown for decorative purposes are called as ornamental plants.
- True.
- False – Cauliflower is used for edible purpose.
- False – Cotton cloth is only suitable for summer season
- False – Sugarcane is used to produce sugar.
![]()
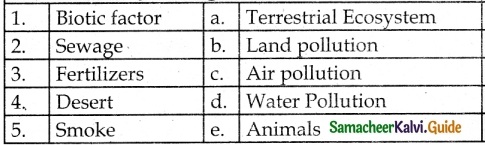
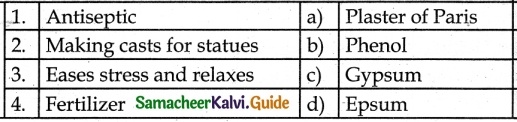
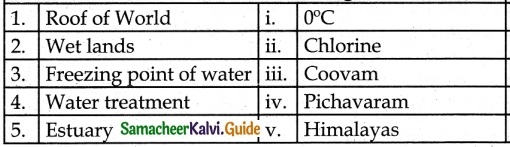
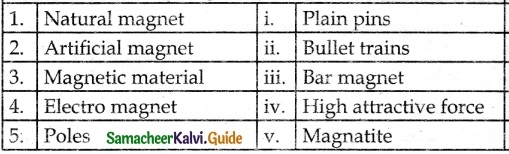
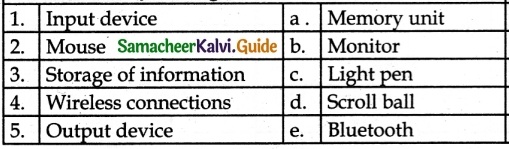
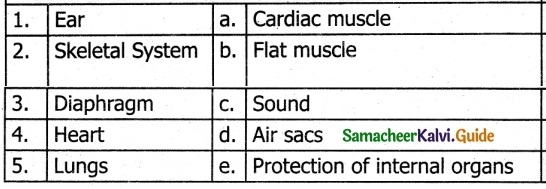
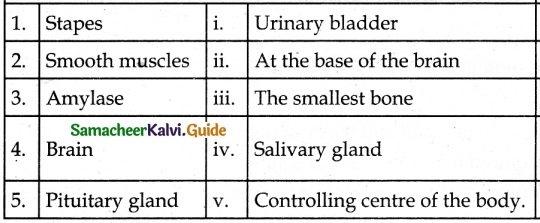
IV. Match the following:
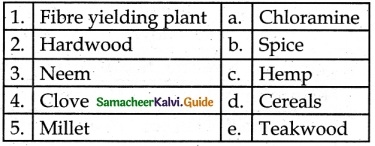
Answer:
1 – c
2 – e
3 – a
4 – b
5 – d
V. Analogy:
- mango : fruit:: maize : ………….
- coconut: fibre :: rose : …………
- bees : pollinate insect:: earthworms : …………
Answer:
- cereal
- essence
- vermicompost producer
VI. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
What is food?
Answer:
Any nutritious substance that people or animals eat or drink or that plants absorb in order to maintain life and growth is called Food.
Question 2.
What are the medicinal plants?
Answer:
Some of the plants around us are good in healing our diseases. We call these plants as medicinal plants.
Question 3.
How hardwood differ from softwood?
Answer:
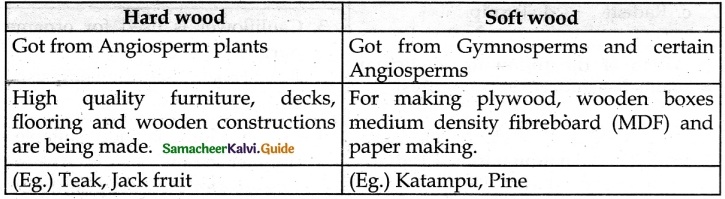
Question 4.
What is Spice?
Answer:
Spices are the aromatic parts of tropical plants traditionally used to flavour food. Bark, roots, leaves, flowers, or stems of certain plants primarily used for flavouring colouring or preserving food.
(Eg.) roots – vetiver,
leaves – curry leaves
seeds – fenugreek
flower bud – clove
![]()
Question 5.
Name any three medicinal plants, which are available in your area?
Answer:

Question 6.
What are the uses of timber?
Answer:
- A timer is used in the construction of buildings, making of furniture
- It is used in making fibreboard, paper making.
VII. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
What is a symbiotic relationship?
Answer:
- The relationship between animals and plants, benefiting both of them is known as a symbiotic relationship.
- (Eg.) Silkworms – feeding on Mulberry leaves – produce silk fibres.
- Honey bee – feed on pollen and honey of plants – Agents of cross-pollination and form vegetables and fruits along with honey.
Question 2.
Write the uses of Neem?
Answer:

Question 3.
Name any five plants and their parts that we eat.
Answer:
- Carrot, Beetroot, and radish – Taproots
- Potato, Ginger, Turmeric – Underground stem
- Curry leaves, Coriander leaves – Leaves
- Drum stick – Leaves, Unripe fruit, and bark.
- Paddy, Wheat, Maize, and Ragi – Seeds
VIII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Write short notes on-Timber yielding plants.
Answer:
Wood is used commercially due to its features like durability, stylish finishing, and resistance to temperature changes.
Timbers can be classified into hardwoods and softwoods.
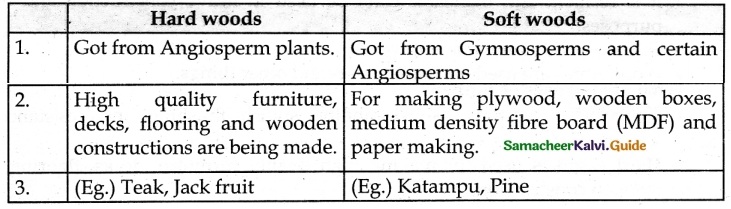
Question 2.
Comment on the importance of plant-animal interaction.
Answer:
The relationship between plants and animals, to get food and shelter etc.
This relationship which is economically significant benefits not only animals but also plants.
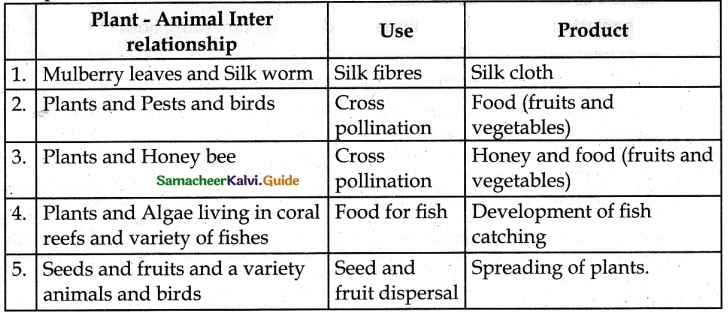
![]()
IX. Questions Based on Higher Order Thinking Skills:
Question 1.
Desert does not have water. Why? Give the reason.
Answer:
- Most deserts get less than 10 inches of rainfall each year.
- The evaporation rate is higher than the rainfall.
- In the desert, there is little water available for plants (cactus-like) and other organisms.
- Cactus like plants and animals living in such areas are adapted to save water and to endure drought.
(Eg.) Cactus Camel etc.
Question 2.
Kavitha said, “Palm tree is a tall tree, so it gives hardwood”! Do you agree with her statement or not? Explain. Why?
Answer:
False. Because:
- Even though they are tall, they produce only softwoods.
- It is resilient and malleable can’t be used in heavy construction and other purposes.
- So the wood is known as softwood.
- Wood fibres are used for making hats and other things.
Question 3.
Look at the diagram given below and answer the following questions.
a. Soil fertility is increased by bacteria How?

Answer:
1. The droppings and shedding of leaves, fruits, and other dead parts of plants degrade in the soil by bacterial and fungal action to form humus-increase soil fertility.
2. Blue-green Algae and Bacteria are extensively used to fix Nitrogen in the soil and increase biofertilizer in the soil for agriculture.
b. Honey bees are essential for the reproduction of the plants Why?

Answer:
- Honey bees suck nectar from flowers and convert it into honey.
- During this process, they carry pollen on their bodies and help plants to do cross-pollination and inturn form vegetables and fruits.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Plants in Daily Life Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the right answer:
Question 1.
Which are the source of food and energy for all living organisms in the world.
(a) Plants only
(b) Plants and animals
(c) Animals only
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Plants only
Question 2.
Aloe ______ is used as a laxative
(a) Roots
(b) Stem
(c) Leaves
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) Leaves
Question 3.
Leaf fibres are got from
(a) Aloe vera
(b) Agave
(c) Coconut
(d) Cotton
Answer:
(b) Agave
Question 4.
We are planting shrubs such as ________ to decorate houses
(a) Mandara
(b) Mullai
(c) Hibiscus
(d) Allamanda
Answer:
(c) Hibiscus
Question 5.
Plants grown or maintained for its aesthetic features are known as
(a) Fibre plants
(b) Medicinal plants
(c) Plants as food
(d) Ornamental plants
Answer:
(d) Ornamental plants
![]()
Question 6.
Bio fuels are less _______ in nature.
(a) Toxic
(b) Economic
(c) Nutrients
(d) Metals
Answer:
(a) Toxic
II. Very Short Answer
Question 1.
Give evidence for the fact that Rice, Wheat, and Millets were cultivated and utilised in the ancient days.
Answer:
- The presence of charred grains in most of the excavation sites is proof of the above fact.
- Also, ancient literature talks about the existence and usage of several crops of economic importance.
Question 2.
Classify plants on the basis of economic values and uses.
Answer:
They are classified into six varieties. They are:
- Plants as food.
- Spice yielding plants,
- Medicinal plants.
- Fibre yielding plants,
- Timber yielding plants.
- Ornamental plants.
Question 3.
Name the states in India with Jute cultivation?
Answer:
West Bengal, Assam, Orissa, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Tripura, and Meghalaya are the seven states producing jute.
Out of the above seven, West Bengal alone produces 50% jute of India.
Question 4.
Name some of the Indian spices.
Answer:
Cardamom, black pepper, curry leaves, fenugreek, fennel, ajwain, bay leaves, cumin, coriander seeds, turmeric, cloves, ginger, nutmeg, and cinnamon.
Question 5.
What are the medicinal plants?
Answer:
The plants that have chemical compounds to destroy disease-causing germs are known as medicinal plants.
Question 6.
Identify the plant part and write about its use?

Answer:
The given diagram is that of cloves the flower buds used as a spice – to flavour food.
![]()
Question 7.
Classify the Fibre yielding plants based on use.
Answer:
- Textile Fibres – Cotton.
- Cordage Fibres – Coconut Fibre.
- Filling Fibres – Silk cotton
Question 8.
Write the importance of rubber?
Answer:
- Rubber is got from the stem latex of the rubber plant.
- Vehicle tyres, wire insulating covers, and many toys and others are produced out of natural rubber.
- It satisfies 80% rubber demand of the world.