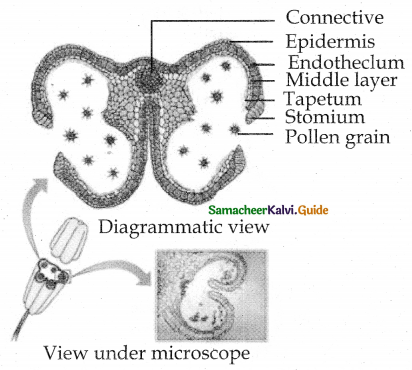
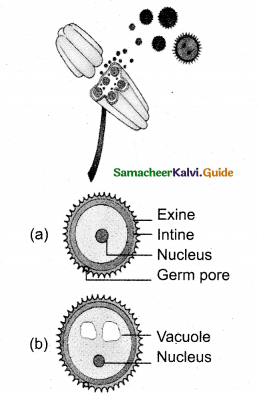
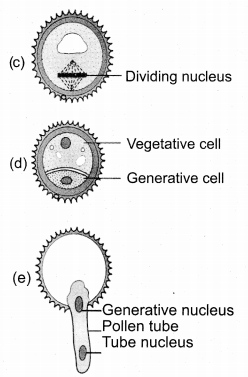
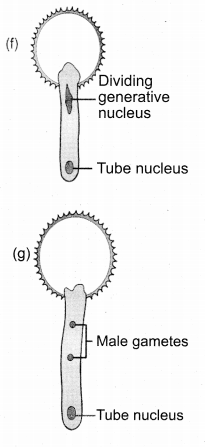
Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th English Guide Pdf Prose Chapter 3 Forgetting Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th English Solutions Prose Chapter 3 Forgetting
11th English Guide Forgetting Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Based on your understanding of the essay, answer the following questions in one or two sentences each:
Question a.
What does Lynd actually wonder at?
Answer:
Robert Lynd wonders at the efficiency of human memory. He is amazed at the ordinary man’s capacity to remember phone numbers, addresses of friends, appointments for lunch and dinner and many names of actors, actresses and leading players in popular games.
Question b.
Name a few things that a person remembers easily.
Answer:
A person remembers telephone numbers, addresses of his friends, dates of good vintages, appointments for lunch and dinner, etc.
Question c.
How do psychologists interpret forgetfulness?
Answer:
Psychologists believe that humans forget what they don’t want to remember, like taking pills.
![]()
Question d.
What is the commonest type of forgetfulness, according to Lynd?
Answer:
According to Lynd the commonest type of forgetfulness occurs in the matter of posting letters.
Question e.
What does the author mean when he says the letter in his pocket leads an unadventurous life?
Answer:
The poet forgets the letters kept in his pocket. Whenever the friend enquires about the unposted letters, it embarrasses him. Then he is forced to produce the evidence of his guilt (i.e.,) the unposted letters. This awkward humiliation is said to be unadventurous.
Question f.
What are the articles the writer forgets most often?
Answer:
The writer forgets books, umbrellas, and walking sticks most often.
Question g.
Who are the citizens of dreamland? Why?
Answer:
Boys who return from cricket and football matches tend to forget bats and balls. Their minds are filled with a vision of the playing field. Their heads are among the stars. They are said to be the citizens of dreamland.
Question h.
What is common about the ‘angler’ and the ‘Poet’?
Answer:
The angler forgets his fishing rod and the poet forgets to post a letter just because their mind is filled with glorious matter.
![]()
2. Based on your reading, answer the following questions in two to four sentences each:
Question a.
What made people wonder about the absentmindedness of their fellow beings?
Answer:
The publication of articles lost by train travellers astonished many readers. Old people did not forget much. In fact, young men have forgotten bats and balls on their return from matches.
Question b.
What are our memories filled with?
Answer:
Our memories are filled with the names of actors and actresses, cricketers, footballers, and murderers.
Question c.
When does human memory work with less than its usual capacity?
Answer:
Human memory works with less than its usual capacity in matters like taking medicine. The author explains that human memory represents the willingness to remember certain things. It forgets what it does not wish to remember. Humans are blessed with “selective amnesia”
Question d.
Why according to Lynd should taking medicines be one of the easiest actions to remember?
Answer:
Taking medicines is one of the easiest actions to remember as it should be taken before, during or after meals. The meal itself is a reminder of it.
![]()
Question e.
How do the chemists make fortunes out of the medicines people forget to take?
Answer:
The forgotten medicines tend to aggravate the illness. Like a vicious cycle, again they are forced to buy costlier medicines. Thus people who forget to take medicines contribute to the fortunes of chemists.
Question f.
The list of articles lost in trains suggests that sportsmen have worse memories than their ordinary serious-minded fellows. Why does Lynd say this?
Answer:
Sportsmen have worse memories as when they return from the game they have their imagination still filled with a vision of the playing field. They are abstracted from the world outside them and their memories prevent them from remembering small prosaic things.
Question g.
What kind of absent-mindedness is regarded as a virtue by Lynd?
Answer:
Scientists, poets, anglers, and philosophers forget prosaic things. Their minds are absorbed in lofty thoughts and glorious imaginations that they forget ordinary things. Socrates, Tagore, and Einstein had the virtue of absent-mindedness. Einstein usually forgot to change his rocks. Once he even forgot his own house address. The absent-mindedness of such great personalities is a virtue. As they make the best of life, they have no time to remember the mediocre.
Question h.
Narrate the plight of the baby on its day out.
Answer:
The baby taken out by its father was left outside a public house just as the father slipped in for a glass of beer. His wife who came shopping saw the baby and took it home deciding to teach a lesson to her husband. To her surprise, the husband came forgetting all about the baby.
![]()
3. Answer the following in a paragraph of about 100-150 words each:
Question a.
You have borrowed a branded cricket bat from your reluctant friend for an outstation match. After returning home you realize you have absent-mindedly left it in the hotel room. Write a letter of apology and regret to your friend.
Answer:
822, Old Peter Road,
Trichy.
Dear Akshay,
Hope this letter of mine would find you in the best of health. First of all, I thank you very much for lending me your branded cricket bat for my match in Chennai. Though you were reluctant at first, you were kind enough to lend it to me later. I really played well with that bat and scored the highest run rate.
Truly it is the luckiest bat. After the match, I kept it safe in the hotel room where I stayed. Because of my weariness, I had a sound sleep that day and was in a hurry to catch my train for the return journey. In that hurry, I forgot to take your bat. Only after reaching Trichy, I realized that I absent-mindedly left your bat in the hotel room itself. I truly regret for the mistake committed by me and beg your pardon.
I know pretty well that it is your precious bat. I am also aware of the fact that you won’t forgive me easily for my action. I have made arrangements to bring back the bat here which may take some time. Kindly bear the inconvenience prevailed and try to forgive me.
With lots of regrets,
Yours affectionately,
Arun.
![]()
Question b.
Kahlil Gibran states ‘Forgetfulness is a form of freedom’ Write an article for your school magazine, linking your ideas logically and giving appropriate examples.
Answer:
Forgetting is deemed by many people leading prosaic lives as a mistake or an inefficiency of mind. But in reality, forgetfulness is freedom. Osho is right in his opinion of forgetfulness. In fact, it liberates painful memories and unpleasant things. We need to “let go” painful memories of the past and be free to aspire for better things in life. Robert Frost in his poem, “Let go” talks about a mediocre person’s inability to let go of things that hurt them. The capacity to forget hurtful memories is a real blessing.
If the human mind does not have the capacity to forget, life would be miserable for every one of us. The human mind is such a wonderful machine that it retains what is most important for personal or professional growth and allows the other things to slip away from the bank of memory. But young ones should remember to remember important assignments, deadlines for submission of homework, examination time-tables, and hall tickets before leaving for examination.
To assist memory we can have a checklist before leaving for school. It is often said, “If you fail to plan, you plan to fail.” So, my dear friends, I appeal to you to love whatever work you do. The brain retains in memory whatever you do with great passion, love, and involvement. For a successful life, a strong memory is indispensable. So, cultivate a strong memory. However, I appeal to you to forget failures, betrayals, and hurts to grow into a happy and healthy person.
“Sometimes we survive by forgetting.”
Question c.
Will you sympathize or ridicule someone who is intensely forgetful? Write an essay justifying your point of view.
Answer:
It is a general fact that all human beings are absent-minded at times. I really sympathize with the person who is intensely forgetful. His extreme level of forgetfulness reveals that he is a creative person and a genius. We have heard of great Scientists who are often forgetful. A person becomes absent-minded based on two facts.
One is when his mind is completely filled with stressful thoughts. Another reason is, he may be a creative person whose mind is always thinking of creating something new and forgets the present. Whatever be the reason there is no use ridiculing them.
On the other hand, we can help or guide them to note down important information in their diaries so that they can see to it when they forget something. In Kahlil Gibran’s point of view “Forgetfulness is a form of freedom”. So it can be rightly concluded that those who enjoy that freedom are really blessed.
![]()
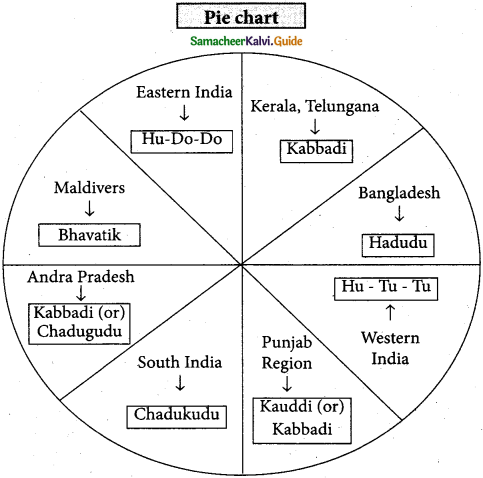
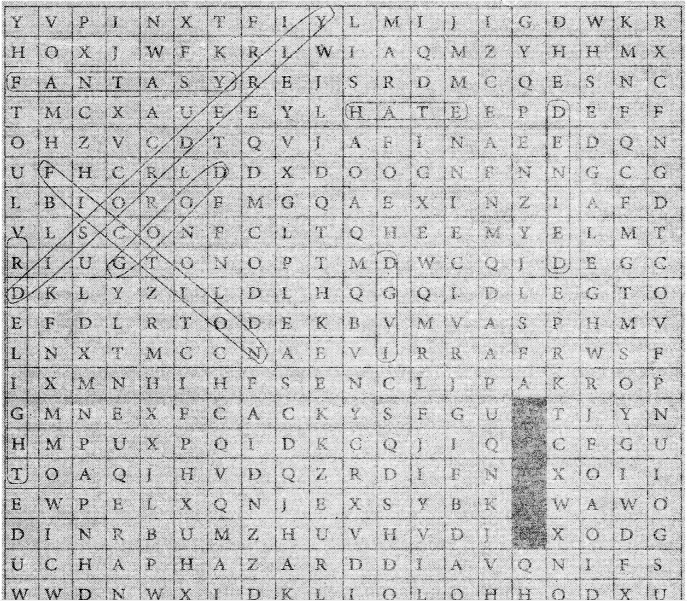
d) Find the antonyms of the following words in the puzzle and shade them with a pencil. The first one has been done for you:
![]()
Answer:
![]()
- Seldom x Often
- admitted x denied
- methodical x disorderly
- reality x fantasy
- fact x fiction.
- virtue x vice
- vile x good
- indignant x delighted
- relish x hate
Now, read the following biographical extract on Sujatha Rangarajan, a Science fiction writer, and answer the questions that follow:
1. Sujatha is the allonym of the Tamil author S. Rangarajan and it is this name that is recognized at once by the Tamil Sci-Fi reading community. You might have seen the Tamil movie ‘Endhiran’ where the robot Chitti exhibits extraordinary talents in an incredible manner. The robot could excel a human being in any act, beyond one’s imagination.
Jeeno, a robotic dog which appeared in Sujatha’s science fiction novel “En Iniya lyandhira” (My Dear Robot) formed the basis of Chitti’s character. Like Chitti, Jeeno was an all-rounder who could cook, clean, and fight. High-tech computer technology terms are used in the story. Jeeno, a pet robot, plays an important role throughout the story. As the story proceeds, it behaves and starts to think on its own like a human and instructs Nila, a human being, on how to proceed further in her crises.
2. In the preface of En lniya Iyandhira the writer states the reason for his attraction to the genre: Science gives us the wonderful freedom to analyse thousands and thousands of alternative possibilities. While using it, and while playing with its new games, a writer needs to be cautious only about one thing. The story should draw some parallels or association from the emotions and desires of the present humankind.
Only then it becomes interesting. Jeeno, the robot dog, was intelligent. But the character became popular only because of the robot’s frequently displayed human tendencies’ It is no wonder that all his works echo these words and will remain etched in the minds of the readers who enjoy reading his novels to have a wonderful lifetime experience.
3. It was Sujatha, who set the trend for sci-fi stories. He had tracked the origin from Mary Shelly’s Frankenstein to his short stories. He has written 50 sci-fi short stories and these were published in various Tamil magazines. His stories have inspired many readers to extend their reading to English sci-fi writers like Isaac Asimov.
The themes were bold, even if there was a dependence on very well – established characterization of English fiction. Sujatha opened up a new world to us with his writings on holograms, computers, and works like ‘En Iniya lyanthira’ inspire many to study computer science.
4. He has been one of the greatest writers for more than four decades. He combined reasoning and science in his writings. Being a multifaceted hi-fi and sci-fi humanistic author, he expressed his views distinctively. He was the one who took Tamil novels to the next level.
As an MIT alumnus and an engineer at BHEL, he was very good at technology. He could narrate sci-fi stories impressively. His readers always enjoyed reading all his detective and sci-fi novels which featured the most famous duo ‘Ganesh’ and ‘Vasanth’.
5. Sujatha has played a crucial role as a playwright for various Tamil movies which have fascinated movie lovers. Hence, it is fathomable that the writer’s perspective of future India enthuses every reader and paves a new way to reading sd-fl stories in English.
![]()
Find words from the passage which mean the same as the following:
Question 1.
difficult to believe (para 1)
Answer:
incredible
Question 2.
a style or category of art, music or literature (para2)
Answer:
genre
Question 3.
having many sides (para 4)
Answer:
multifaceted
Question 4.
capable of being understood (para 5)
Answer:
fathomable.
ஆசிரியரைப் பற்றி:
ராபர்ட் வில்சன் லிண்ட் (1879-1949) ஒரு ஐனஷ் எழுத்தாளர். 20ம் நூற்றாண்டில் வாழ்ந்த கட்டுரையாளர்களில் மிகச்சிறந்தவர். சிறந்த பத்திரிக்கையாளராக தன் பணியைத் தொடங்கினார். தினசரி செய்திதாள்’, ‘புதிய செய்தி, நாடு போன்ற பல பத்திரிக்கைகளில் அதிகமான கட்டுரைகளை எழுதியுள்ளரர்.
தன் படைப்புகள் அனைத்தும் வாசிப்பவரின் ஆர்வத்தை தூண்டக் கூடிய நகைச்சவை, மகிழ்ச்சி, வஞ்சப்புகழ்சி, விமர்சனம் அடிப்படையில் அமைந்திருக்கும்.
1947ல் இவருக்கு குயின்ஸ் பல்கலைக்கழகத்தால் இலக்கியத்திற்கான கௌரவ முனைவர் பட்டம் வழங்கப்பட்டது. இலக்கியத்திற்காக இவருக்கு ராயல் சொனசட்டியால் வெள்ளி பதக்கமும், டைம்ஸ் நிறுவனத்தால் தங்க பதக்கமும் வழங்கப்பட்டது. என்ற இந்த கட்டுரையில் மறதியை பற்றியும், அதன் இயல்பையும் நகைச்சுவையாக எழுதியுள்ளார்.
![]()
பாடத்தைப் பற்றி:
இந்த கட்டுரையில் ராபர்ட் லிண்ட் மனிதர்களில் உள்ள மறதிக்கான அடிப்படைக் காரணங்களைப் பற்றி தெளிவாக கூறுகிறார். நாம் எதை மறந்து போகிறோம், அப்படி மறந்து போவதால் ஏற்படும் விளைவுகள், ஏன் மறந்து போகிறோம் என்று பலவிதமான வினாக்களுக்க விடையையும் தருகிறார். மறத்தலைப் பற்றி தெளிவாக இக்கட்டுரையில் காண்போம்.
Forgetting Summary in Tamil
ரயிலில் செல்லும் பயணிகள் தவரவிட்ட பொருட்களை இப்போது லண்டன் நிலையத்தில் விற்பனைக்கு உள்ளதாக அறிவித்தனர். அதை வாசித்த மக்கள் அவர்கள் மறதி மனப்பாங்கை நினைத்து திகைத்தனர். புள்ளி விவரப்படி நான் சந்தேகப்பட்டது போல் இவ்வாறு மறந்து போகுதல் பொதுவான நிகழ்வுதான்.
இவை மனித நினைவின் திறன் மற்றும் திறன் இல்லாததை சொல்லி அதிசயப்பட வைக்கிறது. நவீன மனிதன் கைபேசி எண்களைக்கூட நினைவில் வைத்திருப்பான். அவன் நண்பரின் முகவரியையும் நினைவில் வைத்திருப்பான். பழங்காலத்தில் நடந்த நல்ல நிகழ்வுகளை கூட அவன் நினைத்துப்பார்க்கிறான்.
மதிய உணவு மற்றும் இரவு சாப்பாட்டிற்கான குறிப்பை அவன் ஞாபகம் வைத்திருப்பான். அவனது நினைவுகள் நடிகர், நடிகைகள், கிரிகிகெட் வீரர்கள் மற்றும் கால்பந்து வீரர்கள் மற்றும் கொள்ளையர்கள் என நெரிசலாக இருக்கும்.
கோடை காலத்தில் அவன் நன்றாக உணவு அருந்திய உயர்ரக ஹோட்டலையும், கடந்து சென்ற ஆகஸ்ட் பருவநிலையும் அவனால் சொல்ல முடியும். அவனது சாதாரண வாழ்விலும், அவன் எதையெல்லாம் நினைவு கூற நினைக்கிறானோ அதை அனைத்தையும் நினைவுப்படுத்துவான்.
லண்டனில் உள்ள ஆண்கள் எல்லோரும் காலையில் ஆடை அணியும் போது தங்களின் ஆடைகளின் சிறு துண்டினை மறப்பதுண்டா? நூற்றில் ஒருவர் கூட இல்லை. ஏன் ஆயிரத்தில் ஒருவர் கூட இல்லை. எத்தனை பேர் வீட்டை விட்டு வெளியில் செல்லும் போது வீட்டின் முன் கதவை அடைக்காமல் செல்வோம்.
![]()
ஒரு நாள் முழுதும் அவ்வாறு போகிறோம், நாம் படுக்கைக்கு செல்லும் வரை நமது செயலை தெளிவாக செய்கிறோம். ஆனால் ஒரு சாதாரண மனிதன் மேல் மாடிக்கு செல்வதற்கு முன் விளக்குகளை அணைக்க மறக்கிறான்.
சில நேரத்தில் நாம் நமது நினைவுகள் சாதாரணமாக செயல்படுவதை விட குறைந்து செயல்படும். ஒரு முதுநிலை மனிதர் மருத்துவர் அவருக்கு பரிந்துரை செய்ததை மறவாமல் எடுத்து செல்கிறார் என நினைக்கிறேன்.
இது ஆச்சரியம் தரக்கூடிய விஷயம் தான். மருந்துகள் என்பது இயல்பாக நம் நினைவில் இருக்கக்கூடியவை. விதியின் அடிப்படையில் அவை சாப்பாட்டிற்கு முன் அல்லது சாப்பாட்டிற்கு பின்பு மற்றும் உணவு என்ன என்பது கூட நினைவில் இருக்கும்.
உண்மை என்னவென்றால் சில ஒழுக்க அரக்கர்கள் அவர்களது மருந்துகளை ஞாபகம் வைத்திருப்பார்கள்.சில உளவியலாளர்கள் நம்மிடம் கூறுவது நாம் மறக்க நினைக்கும் விஷயத்தை மறக்கிறோம், ஏனெனில் அவை மிகுந்த வெறுப்பான மருந்தாக இருக்கும்; மனிதர்கள் குறிப்பிட்ட நேரத்தில் சாப்பிட மறக்கிறார்கள்.
என்னைப்போல் மருந்துக்கு நீண்ட பக்தனாக இருப்பவர்கள் வெறுப்பாக ஆர்வமில்லாமல் (unwillingly) மறந்து விடுகிறோம். புதிய, பரவலாக விளம்பரப்படுத்தப்படும் சிகிச்சை எனக்கு மிகவும் மகிழ்ச்சியளிக்கிறது.
நான் மருந்துகளை என் பையில் வைத்திருந்தாலும், அதை மறந்து, ஒரு மணி நேரம் கழித்து அதை எடுத்து சாப்பிடுவேன். மருத்துவரின் பொக்கிஷம் (fortunes)அவரின் மருந்தை மக்கள் மறந்து சாப்பிடாமல் இருப்பது.
பொதுவாக நான் மறந்துபோவதாக நினைப்பது கடிதம் அனுப்புவதிலே. பொதுவாக என்னை பார்க்க (சந்திக்க) வருபவரிடம் தயக்கத்துடன் எனது முக்கியமான கடிதத்தை அனுப்ப சொல்வேன். கடிதத்தை கொடுக்கும் முன் என் மீது நம்பிக்கை வர வைப்பேன். என்னிடம் கடிதத்தை அனுப்ப சொல்பவர்கள் என்னைப்பற்றி முழுதும் அறியாதவர்கள்.
நானே எடுத்து சென்றாலும் ஒரு பில்லர் பெட்டியை தாண்டிய பிறகு அடுத்த பெட்டியில் போட ஞாபகம் வரும். கையில் வைத்திருப்பது பதிலாக அதை என் சட்டை பையில் வைத்து அப்படியே மறந்துவிடுவேன்.
அதன் பிறகு, இது ஒரு மகிழ்ச்சியில்லா வாழ்க்கை. சங்கிலிப்போன்ற பிரச்சனைகள், எண்ணற்ற சொல்லமுடியா கேள்விகளை கேட்பது போன்று, என்னை வற்புறுத்தி என்னுடைய குற்ற உணர்வுகளை வெளிப்படுத்த வைக்கும்.
இவை அனைத்தும் மற்றவரின் கடிதம் என்பதால் ஈடுபாடு இல்லாமல் இருக்கலாம், சில கடிதங்கள் நான் எழுத நினைத்தது கூட நான் அனுப்ப மறந்துள்ளேன்.
நான் ரயிலில், Taxi யில் பொருட்களை தவறவிட்டவர்களைப் போல மிகச்சிறந்த மறதியாளன் அல்ல. என் புத்தகத்தையும், Walking stick யும் தவிர மற்ற எல்லாவற்றையும் நினைவுபடுத்திக் கொள்வேன். Walking stick வைத்திருப்பது நடக்க கூடிய காரியம் அல்ல. பழையகால ஆசை அதன் மேல் உண்டு, அடிக்கடி நான் அதை வாங்குவேன்.
![]()
எனது நண்பன் வீட்டுக்கு அல்லது ஒரு ரயில் பயணத்திற்கு பிறகு மற்றொன்றை தொலைத்துவிடுவேன். தொலைத்து விடுவேன் என்ற பயத்தில் குடை எடுத்து செல்வதில்லை. வாழ்வில் குடையை நான் தொலைத்தது இல்லை – குள்ளமான குடையை கூட தொலைத்தது உண்டா?
நம்மில் பலர், ஞாபகம் மறதியால் பல பொருட்களை பயணங்களில் இழந்திருக்கிறோம். சாதாரண மனிதன் சேரவேண்டிய இடத்தை அடையும் போது தன் பையையும் பொருளை பத்திரமாக கொண்டு செல்கிறான். அந்த ஆண்டில் ரயிலில் பொருட்களை தவறவிட்டவர்களின் பட்டியலில் பெரும்பாலானோர் இளைஞர்களே. சாதாரண மனிதனை விட விளையாட்டு வீரனுக்கு ஞாபகமின்மை அதிகமாக உள்ளது.
கிரிக்கெட் பேட், கால்பந்து போன்ற எண்ணிலடங்கா பொருட்களே மறக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன. தெளிவாக புரிந்துகொள்ள, ஆண்கள் விளையாடி விட்டு வீடு திரும்பும் போது விளையாட்டு திடலின் நினைவே இருக்கும் – அவர்கள் தலைவர்கள் நட்சத்திரங்கள் மத்தியிலும் – அவர்கள் சிறந்த செயல் (exploit) மற்றும் குறைகளை நினைத்து பார்ப்பார்கள்.
நினைக்க கூடிய (Abstracted) வகையில் உலகம் அவர்களுக்கு வெளியே இருக்கும். நினைவுகளில் சில மந்தமான (Prosaic) செயல்கள் அவர்களுடன் எடுத்து செல்ல நேரிடும்.
மீதி நாட்களில் அவர்கள் கனவு உலகத்தின் குடியுரிமை கொண்டவர்கள். இதேபோல், சந்தேகமின்றி, மீன்பிடிப்பவர்கள் தூண்டிலை மறப்பார்கள். பொதுவாக மீன் பிடிப்பவரை சொல்வது எதன் அடிப்படையில் நியாயப்படுத்த என தெரியவில்லை.
மனிதர்களிள் அவர்கள்தான் கற்பனையாளர்கள், அம்மனிதன் புதிதாக உருவாக்கும் கற்பனையோடு அவன் வீட்டுக்கு செல்லும் போது அது அவன் குணங்களின் சிறு மறதிமனப்பாங்கு தன்மையை காட்டுகிறது.
எதார்த்ததில் மீன் பிடிப்பதை அவர் மறந்துவிட்டு பிறகு Utopia மீன்பிடிப்பை, அச்சத்தை மீறி கற்பனை செய்கிறார். விளையாட்டின் நினைவுகளை மறப்பது நன்மைதான். அவன் மீன்பிடிப்பை மறக்கலாம். ஒருகவிஞன் தனது கடிதத்தை மறக்கலாம், ஏனெனில் அவர் சிந்தனை முற்றிலும் பெருமைக்குரிய விஷயங்கள் நிறைந்திருக்கும்.
மறதிமனப்பான்மை என்னை பொறுத்தவரை சிறந்த குணம்தான். மறதிமனப்பான்மை கொண்டவனது வாழ்க்கை சிறந்ததாக இருக்கும். சாதாரண (mediocre) விஷயங்கள் நினைவுப்படுத்த அவனுக்கு நேரம் இருக்காது. Socrates அல்லது Coleridge நம்பி கடிதத்தை அனுப்ப சொல்வதற்கு சமம்? அவர்களுக்கு செயலில் ஆர்வம் உள்ளது.
கேள்வி என்னவென்றால் நல்ல நினைவுகளை தக்கவைப்பது நல்லது என்று அடிக்கடி பேசப்பட்டு வருகிறது. மனிதனின் தவறான நினைவுகளில் தான் சிறந்தவன் என தோன்றும். அனைத்தும் நினைவில் வைத்திருக்கும் மனிதன் இயந்திரம். அவன் முதல் அறிவாளி என மதிக்கப்படுவான்.
![]()
சில இடங்களில் குழந்தைகள் மற்றும் மனிதரின் சிறந்த நினைவுகளை பேச சிறந்தவன் இல்லை. சிறந்த எழுத்தாளர்கள், இசை உருவாக்குபவர்கள் மொத்தத்தில் மிகுந்த ஆற்றல் கொண்ட நினைவுகள் கொண்டவர்கள் என நான் நினைக்கிறேன். நினைவுகள் தான் அவர்கள் கலையின் பாதி சகாப்தம்.
அடுத்ததாக அரசியல் மேதைகள் முற்றிலும் மோசமான நினைவாற்றால் கொண்டவர்கள். இரண்டு அரசியல் மேதைகளை ஒரே செயலைப்பற்றி பேச செய்தால் என்ன நடக்கும். எடுத்துக்காட்டாக அமைச்சரவைக் கூட்டத்தில் ஒவ்வொருவரும் மற்றொருவர் கதையை உண்மையாக வடித்து (seive) தைரியமாக (grid) உரைப்பார்கள்.
ஒவ்வொரு அரசியல் வாதியின் சுயகுறிப்பு மற்றும் பேச்சு மொழி சவால் நிறைந்ததாக இருக்கும் , இந்த உலகம் இன்னும் சிறந்த அரசியல் வாதியை கொண்டுவரவில்லை. ஒரு சிறந்த கவிஞன் மிகுந்த நினைவாற்றல் மற்றும் புத்திகூர்மை உள்ளவனாக இருக்க வேண்டும்.
அதே நேரத்தில், சிறந்த நினைவாற்றால் கொண்ட மனிதரை மதிக்க வேண்டும். நான் ஒரு அப்பாவை அறிந்தவரை அவர் குழந்தையை (Perambulator) குழந்தைகளுக்கான வண்டியில் வைத்து அதிகாலையில் பொது இடம் ஒன்றுக்கு பீர் அருந்த சென்றார்.
சிறிது நேரம் கழித்து அவரது மனைவி அதே இடத்திற்கு பொருட்களை வாங்க வந்தார். அங்கே அவர் தூங்கிக்கொண்டிருக்கும் அவர் குழந்தையை பார்க்கிறார்.
கணவனின் செயலால் கோபம் (Indignant) கொண்டார். சரியான பாடம் கற்பிக்க நினைத்தாள். அவன் அந்த வண்டியை வீட்டிற்கு கொண்டு சென்றார். அவன் வெளியே வந்து பார்க்கும் போது வண்டி அங்கே இல்லை.
அவன் வீட்டிற்கு சென்றான், கவலையான முகத்துடனும் நடுங்கிய (shivering) உதடுகளுடனும் மனைவி முன் நின்று குழந்தையை திருடிவிட்டார்கள் எனக் கூறினான். அவளுக்கு எப்படி எரிச்சல் (vexation) இருந்திருக்கும். இருந்தும் மதிய உணவின் சில நேரத்திற்கு முன்பு சிரித்தும் சந்தோஷப்படுத்தியும் கேட்டார்.
![]()
சரி, என் அன்பே, இன்று மதிய சாப்பாடு என்ன? அனைத்து நிகழ்வுகளையும் (குழந்தை மற்றும் நடந்த நிகழ்வுகளை) மறந்து விட்டு செயல்பட்டாள். எத்தனை ஆண்கள் ஞானிகள் விட குறைந்த மறதி மனப்பான்மை பெற்றிருப்பார்கள்? என்று நினைத்து நானும் பயப்படுகிறேன்.
புத்திசாலித்தனமாக திறமையான நினைவுகளுடன் நாம் பிறந்திருக்கிறோம், அப்படி இல்லை எனில், எந்த ஒரு நவீன நகரத்திலும் குடும்பத்தின் நிறுவனம் உயிர்வாழ முடியாது.