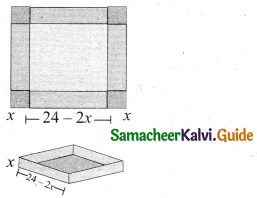
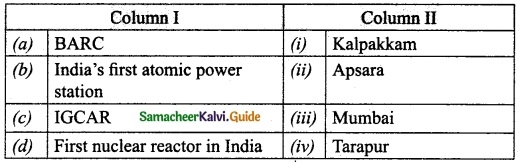
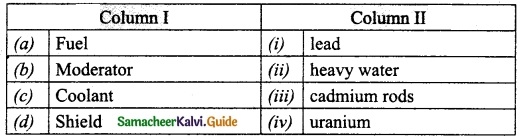
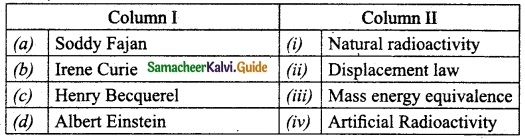
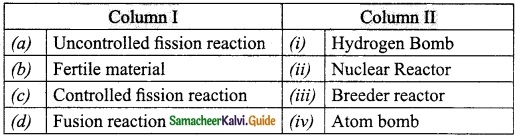
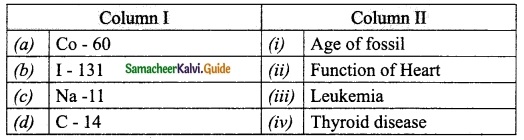
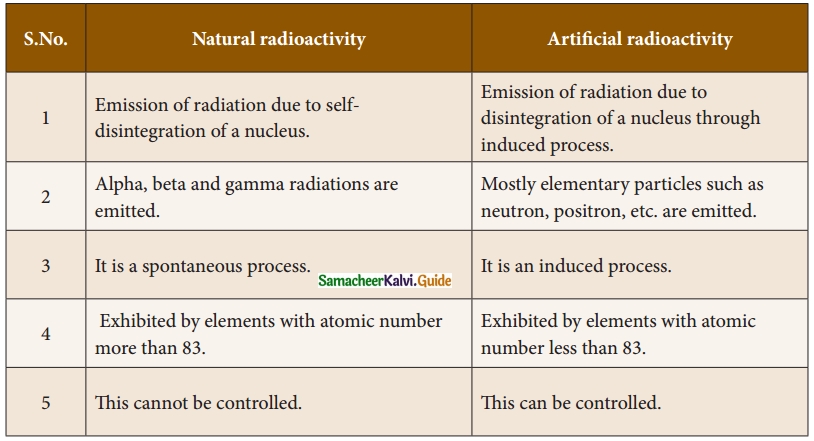
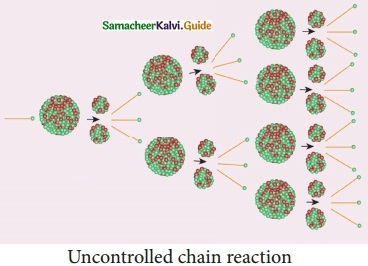
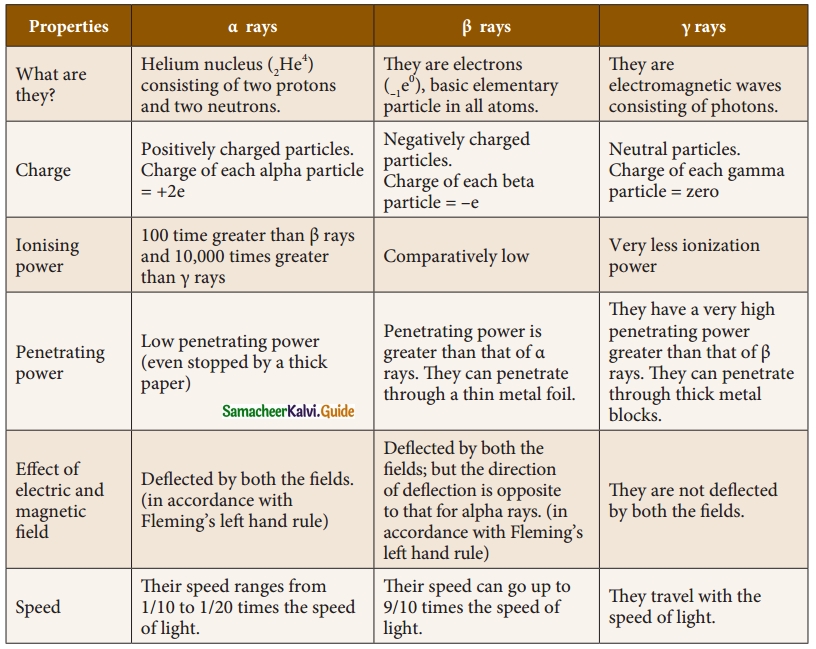
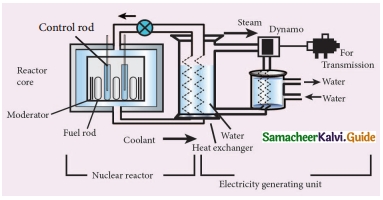
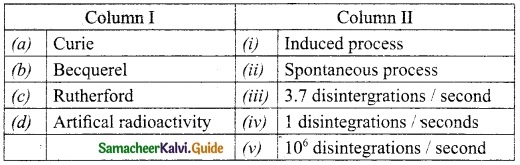
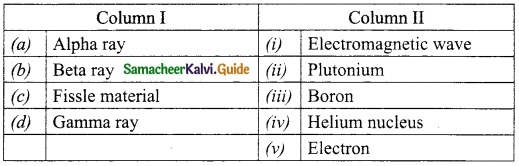
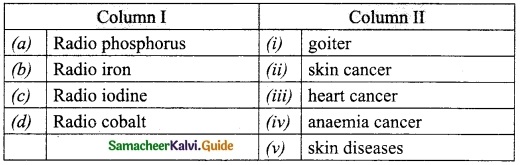
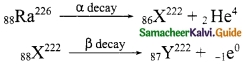
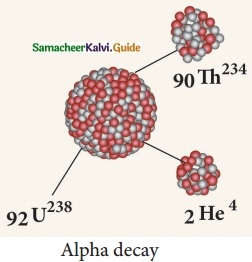
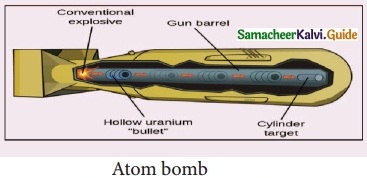
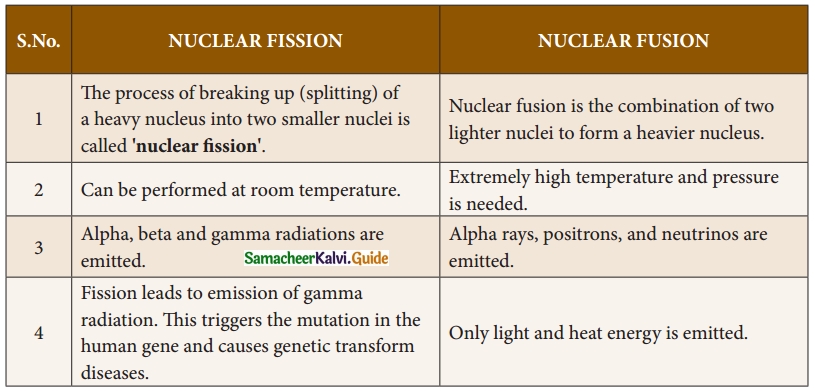
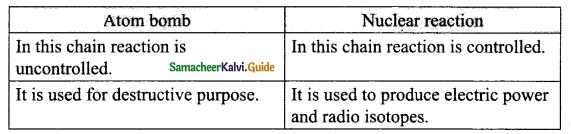
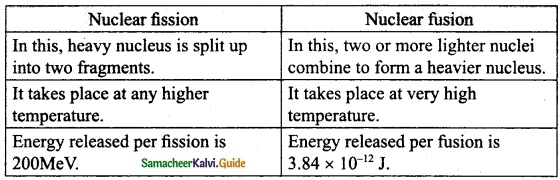
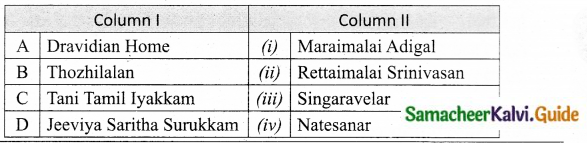
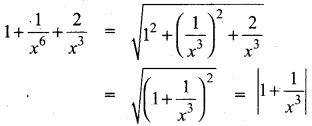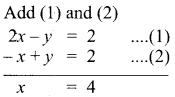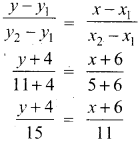Subject Matter Experts at SamacheerKalvi.Guide have created Tamil Nadu State Board Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Book Answers Solutions Guide Pdf Free Download are part of Samacheer Kalvi 10th Books Solutions.
Let us look at these TN State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 10th Std Tamil Guide Pdf of Text Book Back Questions and Answers Term 1, 2, 3, Chapter Wise Important Questions, Study Material, Question Bank, Notes, and revise our understanding of the subject.
Students can also read Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Papers 2020-2021.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Book Solutions Guide Pdf Free Download
Tamilnadu State Board Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Book Back Answers Solutions Guide Term 1, 2, 3.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Book Back Answers
- Chapter 1.1 அன்னை மொழியை
- Chapter 1.2 தமிழ்சொல் வளம்
- Chapter 1.3 இரட்டுற மொழிதல்
- Chapter 1.4 உரைநடையின் அணிநலன்கள்
- Chapter 1.5 எழுத்து சொல்
- Chapter 2.1 கேட்கிறதா ஏன்குரல்!
- Chapter 2.2 காற்றை வா!
- Chapter 2.3 முல்லைப்பாட்டு
- Chapter 2.4 புயலிலே ஒரு தோணி
- Chapter 2.5 தொகைநிலைத் தொடர்கள்
- Chapter 3.1 விருந்து போற்றுதும்!
- Chapter 3.2 காசிக்காண்டம்
- Chapter 3.3 மலைபடுகடாம்
- Chapter 3.4 கோபல்லபுரத்து மக்கள்
- Chapter 3.5 தொகாநிலைத் தொடர்கள்
- Chapter 3.6 திருக்குறள்
- Chapter 4.1 செயற்க்கை நுண்ணறிவு
- Chapter 4.2 பெருமாள் திருமொழி
- Chapter 4.3 பரிபாடல்
- Chapter 4.4 விண்ணைத் தாண்டிய தன்னம்பிக்கை
- Chapter 4.5 இலக்கணம் – பொது
- Chapter 5.1 மொழிபெயர்ப்புக் கல்வி
- Chapter 5.2 நீதி வெண்பா
- Chapter 5.3 திருவிளையாடற் புராணம்
- Chapter 5.4 புதியநம்பிக்கை
- Chapter 5.5 வினா, விடை வகைகள், பொருள்கோள்
- Chapter 6.1 நிகழ்கலை
- Chapter 6.2 பூத்தொடுத்தல்
- Chapter 6.3 முத்துக்குமாரசாமி பிள்ளைத்தமிழ்
- Chapter 6.4 கம்பராமாயணம்
- Chapter 6.5 பாய்ச்சல்
- Chapter 6.6 அகப்பொருள் இலக்கணம்
- Chapter 6.7 திருக்குறள்
- Chapter 7.1 சிற்றகல் ஒளி (தன்வரலாறு)
- Chapter 7.2 ஏர் புதிதா?
- Chapter 7.3 மெய்க்கீர்த்தி
- Chapter 7.4 சிலப்பதிகாரம்
- Chapter 7.5 மங்கையராய்ப் பிறப்பதற்கே…
- Chapter 7.6 புறப்பொருள் இலக்கணம்
- Chapter 8.1 சங்க இலக்கியத்தில் அறம்
- Chapter 8.2 ஞானம்
- Chapter 8.3 காலக்கணிதம்
- Chapter 8.4 இராமானுசர் (நாடகம்)
- Chapter 8.5 பா-வகை, அலகிடுதல்
- Chapter 9.1 ஜெயகாந்தம் (நினைவு இதழ்)
- Chapter 9.2 சித்தாளு
- Chapter 9.3 தேம்பாவணி
- Chapter 9.4 ஒருவன் இருக்கிறான்
- Chapter 9.5 அணி
We hope these Tamilnadu State Board Samacheer Kalvi Class 10th Tamil Book Solutions Answers Guide Pdf Free Download will help you get through your subjective questions in the exam.
Let us know if you have any concerns regarding TN State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 10th Standard Tamil Guide Pdf of Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Chapter Wise Important Questions, Study Material, Question Bank, Notes, drop a comment below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.